Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Kano, Koichi*; Hagiwara, Satoshi*; Igarashi, Takahiro; Otani, Minoru*
Electrochimica Acta, 377, p.138121_1 - 138121_10, 2021/05
Times Cited Count:17 Percentile:69.94(Electrochemistry)We investigated the free corrosion potential at an interface between an Al electrode and an aqueous NaCl solution under acidic conditions via density functional theory combined with the effective screening medium and reference interaction site model (ESM-RISM). The electrode potentials for the anodic and cathodic corrosion reactions were obtained from the grand potential profile as a function of the electron chemical potential at the interface. Thereafter, we determined the free corrosion potential using the Tafel extrapolation method. The results of the free corrosion potential were consistent with previous experimental data. By controlling the pH, we determined the pH dependence of the free corrosion potential, and the results agreed well with the experimental results. Our results indicated that the ESM-RISM method duly described the environmental effect of an acidic solution and precisely determined the free corrosion potential.
Otani, Kyohei; Tsukada, Takashi; Ueno, Fumiyoshi; Kato, Chiaki
Zairyo To Kankyo, 69(9), p.246 - 252, 2020/09
The purpose of this study was to investigate the effect of artificial sea water concentration on the corrosion rate of carbon steel under air/solution alternating condition, and to clarify the corrosion mechanism of carbon steel that changes with artificial seawater concentration. Mass measurements showed that the corrosion rate of carbon steel in the alternating condition accelerates with increasing concentration in the concentration region between deionized water to 200 times diluted artificial seawater (ASW), and the corrosion rate decreases with increasing concentration in the concentration region between 20 times diluted ASW to undiluted ASW. It can be considered that the reason why the carbon steel corrosion was suppressed in highly concentrated artificial seawater would Mg ions and Ca ions in the artificial seawater precipitate and cover on the surface due to the increase in pH near the surface by oxygen reduction reaction.
Kato, Chiaki
Comprehensive Nuclear Materials, 2nd Edition, Vol.4, p.528 - 563, 2020/08
In spent fuel reprocessing plants, various nitric media are encountered throughout the PUREX process, used in the separation of fission products, uranium, and plutonium. The PUREX process is thus highly corrosive as it takes place at high temperatures under high concentrations of nitric acid solution containing oxidizing metal ions from spent fuel. In this review, the unique chemical properties of nitric acid are first described. Secondly, the process of oxidizing power generation in boiling nitric acid under heat transfer is described using the redox potential and a thermodynamic model of boiling nitric acid. Finally, the corrosion behavior and corrosion acceleration mechanism specific to the reprocessing environments are described from the perspective of solution chemistry.
Ueno, Fumiyoshi
Zairyo To Kankyo, 68(1), p.2 - 8, 2019/01
It is important to control the cooling water of light water reactors (boiling water reactor and pressurized water reactor) to suitable quality in order to reduce corrosion of structural materials and generation of radioactive corrosion products. For that purpose, monitoring of water quality using electrochemical measurement method is necessary. In this article, the application of ECP measurement to BWR is mainly focused, I describe the water quality of light water reactors and the necessity of electrochemical measurement.
Hanawa, Satoshi; Uchida, Shunsuke; Hata, Kuniki; Chimi, Yasuhiro; Kasahara, Shigeki*; Nishiyama, Yutaka
Proceedings of 20th Nuclear Plant Chemistry International Conference (NPC 2016) (USB Flash Drive), 11 Pages, 2016/10
ECP is the exclusive index to evaluate corrosion condition directly at the points of interest in the mixing of neutron and  -ray environment. ECP can be calculated through the combination of water radiolysis and ECP model. A water radiolysis model have been applied to experiments performed in in-pile loops in the experimental reactors and applicability was confirmed. An ECP model based on the Butler-Volmer equation was also prepared. ECP of stainless steel was measured under well controlled water chemistry condition in in-pile loop in the Halden reactor, and the model was applied to evaluate ECP measured in the Halden reactor. The measured data were well explained by the water radiolysis calculation and ECP model. Accumulation of in-pile ECP data are expected for further validation of the models.
-ray environment. ECP can be calculated through the combination of water radiolysis and ECP model. A water radiolysis model have been applied to experiments performed in in-pile loops in the experimental reactors and applicability was confirmed. An ECP model based on the Butler-Volmer equation was also prepared. ECP of stainless steel was measured under well controlled water chemistry condition in in-pile loop in the Halden reactor, and the model was applied to evaluate ECP measured in the Halden reactor. The measured data were well explained by the water radiolysis calculation and ECP model. Accumulation of in-pile ECP data are expected for further validation of the models.
Holland, M. K.*; Cordaro, J. V.*; Morales-Arteaga, M. E.*; Yamamoto, Masahiko; Kuno, Takehiko; Surugaya, Naoki
Proceedings of INMM 57th Annual Meeting (Internet), 10 Pages, 2016/07
Since 2007, the laboratory at the Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) and Savannah River National Laboratory (SRNL) have collaborated on a new mission to apply controlled-potential coulometry as a primary method for characterizating plutonium master solutions. Measurement results are being used to prepare traceable and certifiable large-size dry (LSD) spike standards for safeguards measurements by isotope dilution mass spectrometry. The collaboration activities performed by JAEA and SRNL were authorized and funded under the JAEA & United States NNSA/DOE Permanent Coordinating Group. This report will chronicle the collaboration activities of JAEA and SRNL, and provide the detail on the periodic coulometer component calibration, the coulometric plutonium measures and measure practices, including the uncertainty propagation for the most recent plutonium master solution used for LSD Spike preparation.
Kato, Chiaki; Sato, Tomonori; Ueno, Fumiyoshi; Yamagishi, Isao; Yamamoto, Masahiro
Zairyo To Kankyo 2015 Koenshu (CD-ROM), p.83 - 86, 2015/05
In relation to the consideration for long-term storage of spent Cs adsorption vessels containing zeolites in the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station, corrosion of the vessel material in the spent Cs adsorption vessel is one of important issues. We performed electrochemical tests of stainless steel (SUS 316L) in the zeolites containing artificial seawater under gamma-ray irradiation. The spontaneous potential (ESP) and critical pitting potential (VC), of SUS316L were measured to understand the corrosion resistance of the stainless steel in this study. The rest potential of the stainless steel increased with increasing time after gamma-ray irradiation. The ESP, defined as the steady rest potential, increased with increasing dose rate, while increasing ESP was suppressed by contact with the zeolites. Concentration of H O
O in bulk water increased with increasing dose rate. The concentration increasing was suppressed by contact with the zeolites due to decomposition of H
in bulk water increased with increasing dose rate. The concentration increasing was suppressed by contact with the zeolites due to decomposition of H O
O . There was good relationship between ESP and the concentration of H
. There was good relationship between ESP and the concentration of H O
O . The VC of SUS316L contacted with the zeolites decreased with increasing Cl
. The VC of SUS316L contacted with the zeolites decreased with increasing Cl ion concentration and is slightly smaller than the VC in the bulk water. The contact with the zeolites causes the suppressant of increasing ESP under the irradiation. The contact with the zeolites can reduce probability in the localized corrosion for SUS316L.
ion concentration and is slightly smaller than the VC in the bulk water. The contact with the zeolites causes the suppressant of increasing ESP under the irradiation. The contact with the zeolites can reduce probability in the localized corrosion for SUS316L.
Shirai, Osamu*; Yamana, Hajimu*; Arai, Yasuo
Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 408-412, p.1267 - 1273, 2006/02
Times Cited Count:41 Percentile:84.4(Chemistry, Physical)no abstracts in English
Tsukada, Takashi; Miwa, Yukio; Ugachi, Hirokazu; Matsui, Yoshinori; Itabashi, Yukio; Nagata, Nobuaki*; Dozaki, Koji*
Proceedings of International Conference on Water Chemistry of Nuclear Reactor Systems (CD-ROM), 5 Pages, 2004/10
IASCC initiation and propagation tests will be performed on the per-irradiated specimen in the Japan Materials Testing Reactor (JMTR). Since in core, the radiolysis of water causes a generation of various kind of radical species and some oxidizing species such as hydrogen peroxide, the water chemistry in irradiation capsules must be assessed by measurements of the electrochemical corrosion potential (ECP). For the in-core measurement of ECP in JMTR, we fabricated and tested the Fe/Fe O
O type ECP sensor. After the fabrication, the function of each sensor was examined in high temperature water by out-of-core thermal cycling and high temperature holding tests.
type ECP sensor. After the fabrication, the function of each sensor was examined in high temperature water by out-of-core thermal cycling and high temperature holding tests.
Laird, J. S.; Hirao, Toshio; Onoda, Shinobu*; Kamiya, Tomihiro
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 219-220, p.1015 - 1021, 2004/06
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:45.06(Instruments & Instrumentation)no abstracts in English
Kato, Chiaki; Yano, Masaya*; Kiuchi, Kiyoshi; Sugimoto, Katsuhisa*
Corrosion Engineering, 52(1), p.53 - 67, 2003/01
The effects of heat-transfer on the corrosion of zirconium was examined in boiling nitric acid solutions with various concentrations. Corrosion mass losses and electrochemical polarization curves were measured on the heat-transfer and isothermal surfaces in the solutions. It was found that the corrosion rate of zirconium was higher on the heat-transfer surface than that on the isothermal surface. The rate increased with increasing nitric acid concentration and solution temperature. The increased oxidization potential on the heat-transfer surface is attributed to the reduction of nitrous acid concentration by the thermal decomposition on the surface and the removal of the decomposition product from solution by boiling bubbles. The redox potential of 12 mol/dm nitric acid on a boiling heat-transfer surface was very close to the breakdown potential of primary passivity of zirconium. This suggests the initiation of SCC on a boiling heat-transfer surface in a nuclear fuel reprocessing.
nitric acid on a boiling heat-transfer surface was very close to the breakdown potential of primary passivity of zirconium. This suggests the initiation of SCC on a boiling heat-transfer surface in a nuclear fuel reprocessing.
Kato, Chiaki; Kiuchi, Kiyoshi; Sugimoto, Katsuhisa*
Corrosion Engineering, 52(1), p.69 - 85, 2003/01
It is necessary to know the generation mechanism of high equilibrium potential in the solutions. Existing nitrogen oxides in nitric acid solutions were first analyzed by Raman spectroscopy and then existing amount of nitrogen oxides were examined by thermodynamic calculation using the SOLGASMIX software. The Raman spectroscopic analysis showed that the existing amount of un-dissociated HNO increased with increasing nitric acid concentration and solution temperature. The thermodynamic calculation showed that the important nitrogen oxides in nitric acid solutions are HNO
increased with increasing nitric acid concentration and solution temperature. The thermodynamic calculation showed that the important nitrogen oxides in nitric acid solutions are HNO , NO
, NO
 , HNO
, HNO , NO
, NO , and NO. The equilibrium potential of nitric acid solutions is, however, mainly decided by the HNO
, and NO. The equilibrium potential of nitric acid solutions is, however, mainly decided by the HNO /HNO
/HNO equilibrium. The thermodynamic calculation also suggested that the increased oxidization potential on the heat-transfer surface is attributed to the reduction of nitrous acid concentration by the thermal decomposition of nitrous acid on the surface and the continuous removal of decomposition product from the solutions by boiling bubbles.
equilibrium. The thermodynamic calculation also suggested that the increased oxidization potential on the heat-transfer surface is attributed to the reduction of nitrous acid concentration by the thermal decomposition of nitrous acid on the surface and the continuous removal of decomposition product from the solutions by boiling bubbles.
Kato, Chiaki; Yano, Masaya*; Kiuchi, Kiyoshi; Sugimoto, Katsuhisa*
Zairyo To Kankyo, 52(1), p.35 - 43, 2003/01
The effects of heat-transfer on the corrosion of zirconium was examined in boiling nitric acid solutions with various concentrations. Corrosion mass losses and electrochemical polarization curves were measured on the heat-transfer and isothermal surfaces in the solutions. It was found that the corrosion rate of zirconium was higher on the heat-transfer surface than that on the isothermal surface. The rate increased with increasing nitric acid concentration and solution temperature. The increased oxidization potential on the heat-transfer surface is attributed to the reduction of nitrous acid concentration by the thermal decomposition on the surface and the removal of the decomposition product from solution by boiling bubbles. The redox potential of 12 mol/dm3 nitric acid on a boiling heat-transfer surface was very close to the breakdown potential of primary passivity of zirconium. This suggests the initiation of SCC on a boiling heat-transfer surface in a nuclear fuel reprocessing.
Kato, Chiaki; Kiuchi, Kiyoshi; Sugimoto, Katsuhisa*
Zairyo To Kankyo, 52(1), p.44 - 52, 2003/01
In order to understand corrosion of metals in nitric acid solutions, it is necessary to know the generation mechanism of high equilibrium potential in the solutions, especially under boiling conditions. The Raman spectroscopic analysis showed that the existing amount of un-dissociated HNO increased with increasing nitric acid concentration and solution temperature. The existing amount of NO
increased with increasing nitric acid concentration and solution temperature. The existing amount of NO also increased by thermal decomposition. The thermodynamic calculation showed that the important nitrogen oxides in nitric acid solutions are HNO
also increased by thermal decomposition. The thermodynamic calculation showed that the important nitrogen oxides in nitric acid solutions are HNO , NO
, NO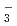 , HNO
, HNO , NO
, NO , and NO. The equilibrium potential of nitric acid solutions is, however, mainly decided by the HNO
, and NO. The equilibrium potential of nitric acid solutions is, however, mainly decided by the HNO /HNO
/HNO equilibrium. The thermodynamic calculation also suggested that the increased oxidization potential on the heat-transfer surface is attributed to the reduction of nitrous acid concentration by the thermal decomposition of nitrous acid on the surface and the continuous removal of decomposition product from the solutions by boiling bubbles.
equilibrium. The thermodynamic calculation also suggested that the increased oxidization potential on the heat-transfer surface is attributed to the reduction of nitrous acid concentration by the thermal decomposition of nitrous acid on the surface and the continuous removal of decomposition product from the solutions by boiling bubbles.
Shirai, Osamu*; Yamana, Hajimu*; Iwai, Takashi; Arai, Yasuo
Proceedings of Nuclear Fuel Cycle Technologies Closing the Fuel Cycle (CD-ROM), 7 Pages, 2003/00
no abstracts in English
Kitatsuji, Yoshihiro; Aoyagi, Hisao; Kimura, Takaumi; Yoshida, Zenko; Kudo, Hiroshi*; Kihara, Sorin*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 39(Suppl.3), p.259 - 262, 2002/11
Controlled-potential electrolysis (CPE) method for the transfer of an ion at the interface of two immiscible electrolyte solutions has been developed. The CPE method was applied to the transfer of actinide ions such as UO
 and Am
and Am between aqueous (W) and nitrobenzene (NB) solutions. The transfer of actinide ions from W to NB facilitated by bis(diphenyl-phosphoryl)methane (BDPPM) was studied, and it was found that CPE was successfully applied to the electrolytic separation of U(VI) and Am(III) from W to NB containing BDPPM.
between aqueous (W) and nitrobenzene (NB) solutions. The transfer of actinide ions from W to NB facilitated by bis(diphenyl-phosphoryl)methane (BDPPM) was studied, and it was found that CPE was successfully applied to the electrolytic separation of U(VI) and Am(III) from W to NB containing BDPPM.
Kitatsuji, Yoshihiro; Yoshida, Zenko; Kudo, Hiroshi*; Kihara, Sorin*
Journal of Electroanalytical Chemistry, 520(1-2), p.133 - 144, 2002/02
no abstracts in English
Miura, Yukitoshi; Ido, Takeshi*; Kamiya, Kensaku; Hamada, Yasuji*; JFT-2M Group
Nuclear Fusion, 41(8), p.973 - 979, 2001/08
Times Cited Count:17 Percentile:47.27(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)no abstracts in English
Mine, Tatsuya*; Mihara, Morihiro;
JNC TN8430 2000-009, 35 Pages, 2000/07
In the geological disposal system of TRU wastes, nitrogen generation by denitrifying bacteria could provide significant impact on the assessment of this system, because nitrate contained in process concentrated liquid waste might be electron acceptor for denitrifying bacteria. In this study, the activities and tolerance of denitrifying bacteria under disposal condition were investigated. pseudomonas denitrificans as denitrifying bacteria was used. The results showed that Pseudomonas denitrificans had activity under reducing condition, but under high pH condition (PH 9.5), the activity of Pseudomonas denitrificans was not detected. It is possible that the activity of Pseudomonas denitrificans would be low under disposal condition.
9.5), the activity of Pseudomonas denitrificans was not detected. It is possible that the activity of Pseudomonas denitrificans would be low under disposal condition.
Ido, Tsuyoshi; Kamiya, Kensaku; Miura, Yukitoshi; Hamada, Yasuji*; Nishizawa, Akimitsu*; Kawasumi, Yoshiaki*
Plasma Physics and Controlled Fusion, 42(5A), p.A309 - A315, 2000/05
Times Cited Count:18 Percentile:47.9(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)no abstracts in English